How to use
Global view
The user can move to the country-specific simulation screen by selecting any country from the global map. The country can be selected directly from the pull-down or the map.
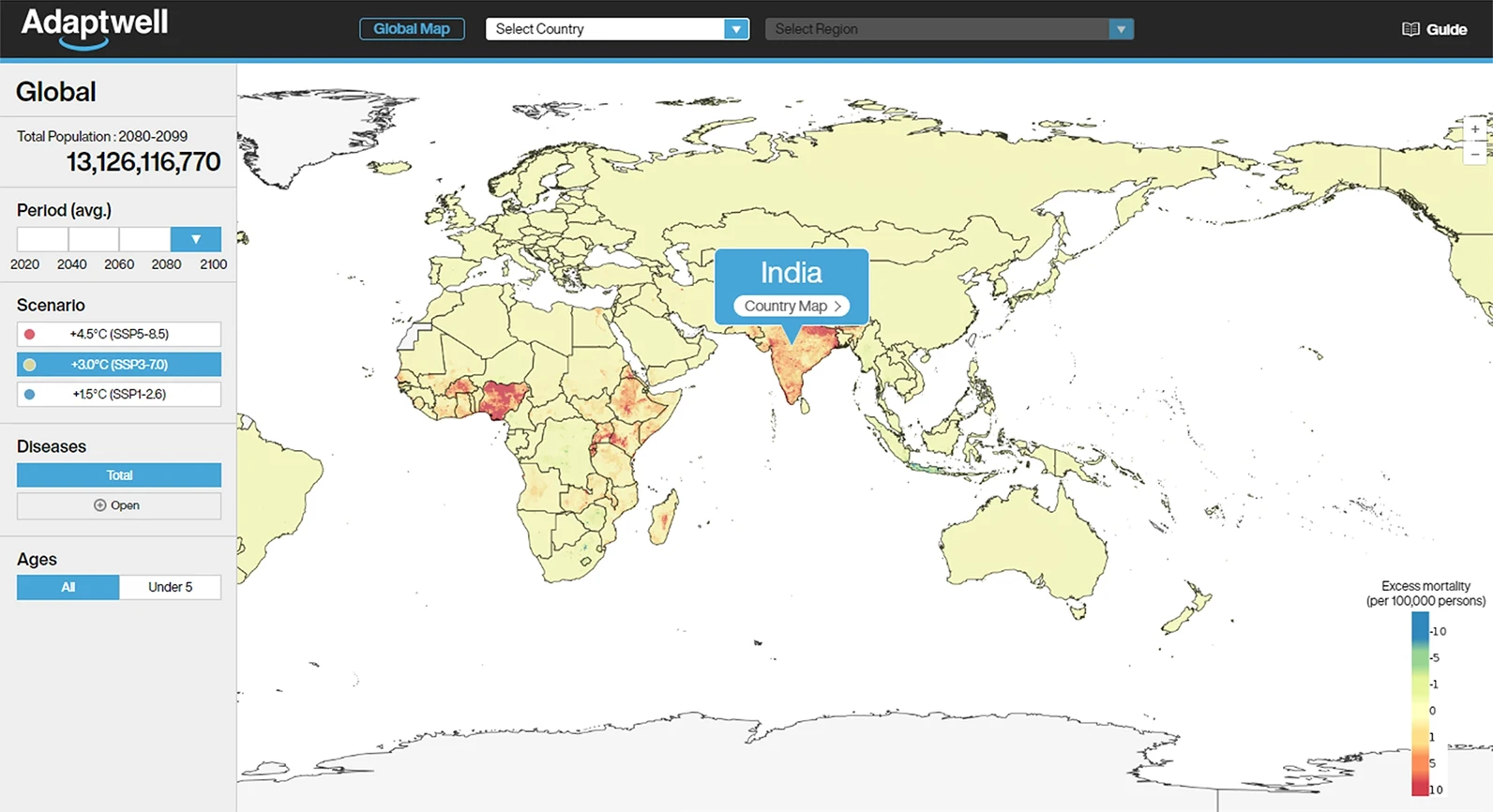
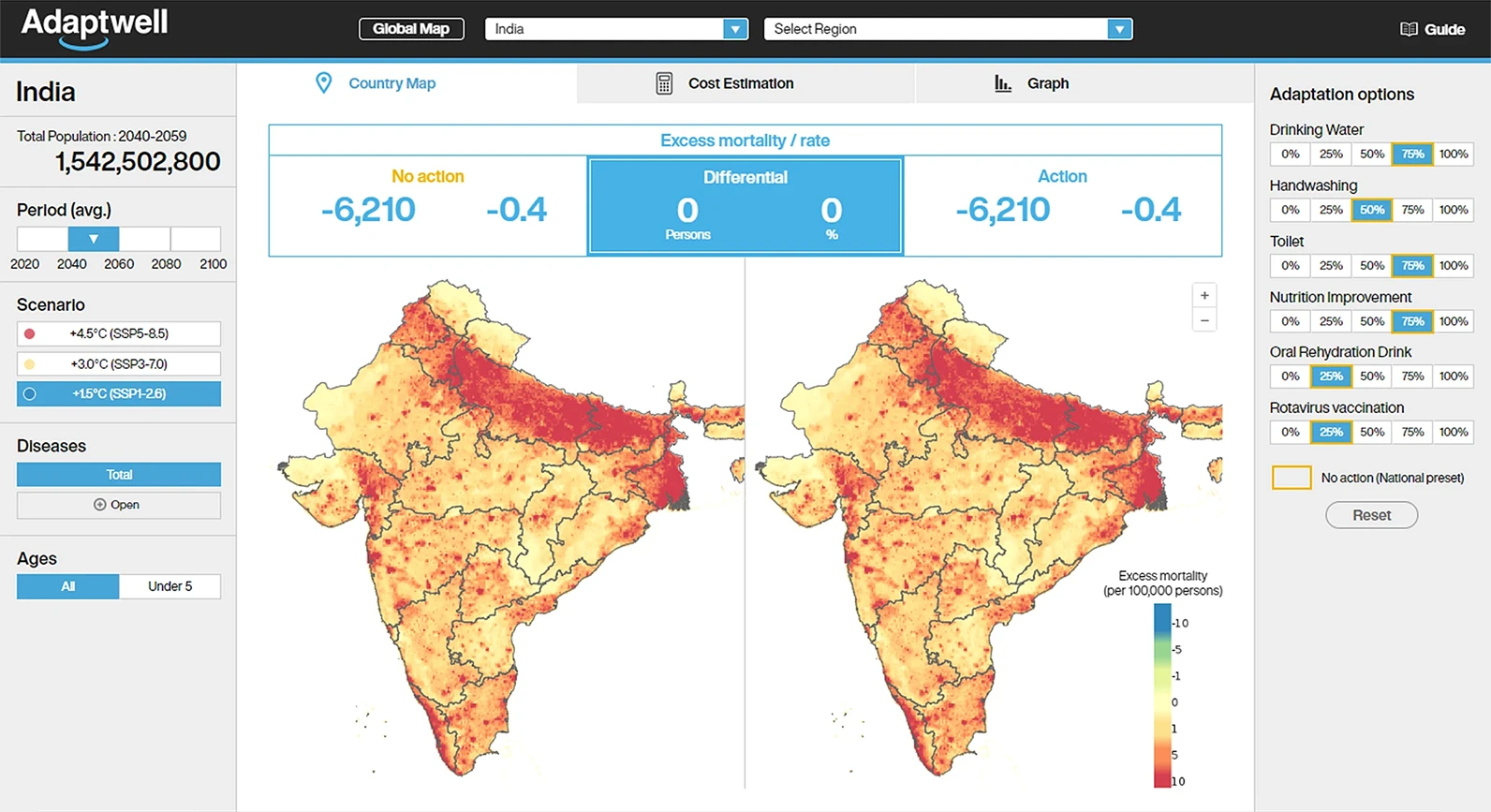
Country view
The user can display simulation results on country-specific page by selecting the multiple conditions. Selectable conditions include the time period, types of pathogen, SSP scenarios, adaptation preset, adaptation for each pathogens, and a cost estimation function for adaptations. Selected conditions are available for data export.
Time period
Users can select the arbitrary ten years between the 2020s to 2090s.
Type of pathogens
Any one of ten different pathogens can be selected.
SSP scenario
Any one of the five options from SSP1 to SSP5 can be selected.
Adaptation preset and Adaptation
Users can select any adaptation presets, reducing the burden of entering initial values for adaptation combinations. Furthermore, the presets can be customized based on the presets.
Decision making support
Users can use the cost estimation function to implement each adaptation measure to analyze the cost-benefit analysis of the investment based on the difference between willingness to pay and costs.
Data export
Selected conditions are available for data export.
Terminology
Adaptation
Adaptation for climate change
The process of adjustment to actual or expected climate and its effects. In human systems, adaptation seeks to moderate harm or exploit beneficial opportunities. In natural systems, human intervention may facilitate adjustment to expected climate and its effects.
(Source: Definition of Terms Used Within the DDC Pages, IPCC Data Distribution Center)
https://www.ipcc-data.org/guidelines/pages/glossary/glossary_a.html (refer: 20230731)
Adaptation for waterborne diseases
The projection modelling considered the combination of better socio-economic growth (relates to more financing for healthcare), less exposure to unsafe drinking water, poor sanitation, and better nutrition in children.
(Source: Chua et al. 2021; DOI: 10.1016/S2542-5196(21)00152-2)
- Drinking water
- Handwashing facilities
- Sanitation facilities
- Nutrition facilities
- Oral rehydration solution (ORS)
- Rotavirus vaccination
Climate change
Climate change refers to a change in the state of the climate that can be identified (e.g., by using statistical tests) by changes in the mean and/or the variability of its properties, and that persists for an extended period, typically decades or longer. Climate change may be due to natural internal processes or external forcings such as modulations of the solar cycles, volcanic eruptions and persistent anthropogenic changes in the composition of the atmosphere or in land use.
(Source: Definition of Terms Used Within the DDC Pages, IPCC Data Distribution Center) https://www.ipcc-data.org/guidelines/pages/glossary/glossary_c.html (refer: 20221013)
Diarrheal pathogens
Bacteria, virus, and protozoa causing diarrheal diseases such as norovirus and cholera etc.
- Norovirus
- Rotavirus
- Shigella
- Typhoid
- Campylobacter
- Cholera
- Non-typhoidal Salmonella
- Enteropathogenic E. coli
- Enterotoxigenic E. coli
- Cryptosporidium
Excess mortality
Excess mortality is defined as the difference between the total number of deaths estimated for a specific place and given time period and the number that would have been expected in the absence of a crisis.
(Source: WHO) https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/global-excess-deaths-associated-with-the-COVID-19-pandemic (refer: 221014)
GCM
GCM stands for Global Climate Model.
The model representing physical processes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and land surface, are the most advanced tools currently available for simulating the response of the global climate system to increasing greenhouse gas concentrations.
(Source: Definition of Terms Used Within the DDC Pages, IPCC Data Distribution Center) https://www.ipcc-data.org/guidelines/pages/gcm_guide.html (refer: 20221013)
RCP
RCP stands for Representative Concentration Pathways.
Scenarios that include time series of emissions and concentrations of the full suite of greenhouse gases (GHGs) and aerosols and chemically active gases, as well as land use/land cover (Moss et al., 2008). The word representative signifies that each RCP provides only one of many possible scenarios that would lead to the specific radiative forcing characteristics. There are four scenarios; RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6.0, and RCP8.5.
(Source: Definition of Terms Used Within the DDC Pages, IPCC Data Distribution Center) https://www.ipcc-data.org/guidelines/pages/glossary/glossary_r.html (refer: 20221013)
SSP
SSP stands for Shared Socioeconomic Pathways.
Scenarios of global development focus on the uncertainty in future societal conditions, describing societal futures that can be combined with climate change projections and climate policy assumptions to produce integrated scenarios to explore mitigation, adaptation and residual climate impacts in a consistent framework.
(Source: O’Neill et al 2016; DOI: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.01.004)
Waterborne disease
Waterborne disease is an illness transmitted via contaminated water which contains pathogenic viruses, bacteria, etc.
Reference
Chua PLC, Huber V, Ng CFS, Seposo XT, Madaniyazi L, Hales S, Woodward A, Hashizume M. Global projections of temperature-attributable mortality due to enteric infections: a modelling study. Lancet Planet Health. 2021;5(7):e436-e445. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(21)00152-2.
Chua PLC, Ng CFS, Tobias A, Seposo XT, Hashizume M. Associations between ambient temperature and enteric infections by pathogen: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Planet Health. 2022 Mar;6(3):e202-e218. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00003-1.
Disclaimer
This website was developed by the University of Tokyo and Pacific Consultants Ltd., sponsored by the Ministry of the Environment.
The University of Tokyo, Pacific Consultants Co., LTD., and Ministry of Environment bear absolutely no responsibility for any act and the results taken by the user involving the use of the Website (including the use of information) The Content may be modified, moved or deleted without prior notice.
Map disclaimer
The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Ministry of Environment Government of Japan concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries.
 Guide
Guide