SCROLL
Global excess mortality
0
Waterborne diseases pessimistic scenario up to the year 2100.
Our value
The Adaptwell provides simulation results based on the selected conditions
for making decisions regarding implementing waterborne diseases adaptations.
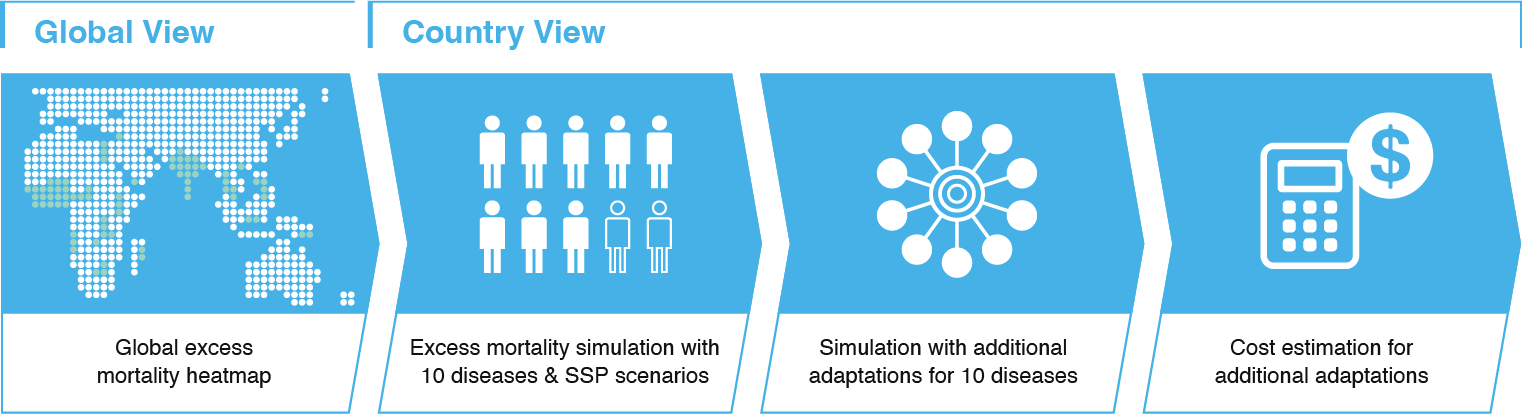
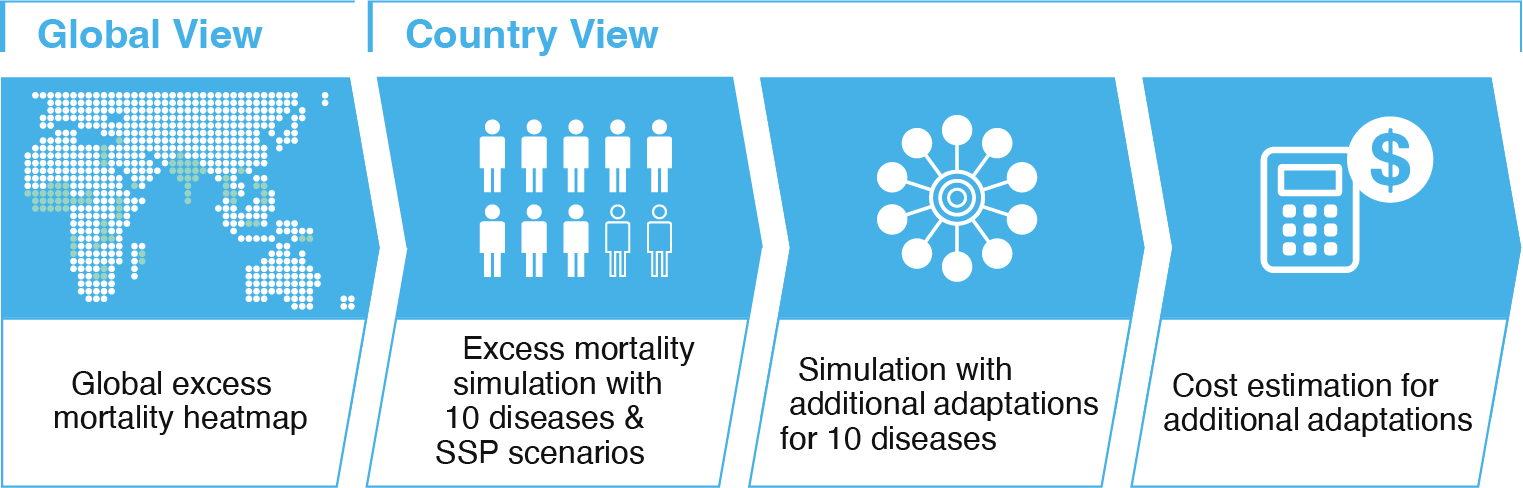
Your action
Six typical measures for reducing waterborne diseases.
Drinking Water
2.2 billion
2.2 billion people in urban areas still do not have access to safe drinking water. Facilitating safe and clean drinking water prevents serious waterborne diseases.
Handwashing
653 million
653 million people have no handwashing facility. Basic hygiene services keep children and families healthy.
Toilet
3.4 billion
3.4 billion people still do not have safely managed toilets. Installation of proper toilets for all households and educational institutions prevents the spread of waterborne diseases.
Nutrition Improvement
200 million
200 million children (under five) suffer from malnutrition . Improving and sustaining nutrition programmes will help ensure enough food and nutrition.
Oral Rehydration Drink
400,000 ++
More than 400,000 children (under five) die each year from diarrheal diseases. Oral rehydration drinks are noteworthy treatment for children who suffer from diarrhoea to prevent dehydration.
Rotavirus Vaccination
500,000 ++
More than 500,000 children (especially under one) have died from rotavirus before the introduction of rotavirus vaccinations in 2006. Vaccination promotion can dramatically reduce child mortality from rotaviral infection.




